Solar Grading for Off-Grid Applications:
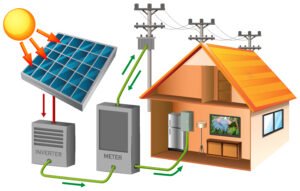
Solar grading for off-grid applications involves evaluating and selecting solar panels and related components based on specific criteria to ensure optimal performance in off-grid scenarios. Off-grid applications typically refer to systems that operate independently of the traditional electrical grid, such as remote cabins, RVs, boats, or emergency backup systems. Here are some key considerations for solar grading in off-grid applications:
Energy Requirements:
Calculate the daily energy consumption of the off-grid system. This will help determine the size and capacity of the solar power system needed to meet the specific energy needs.
Solar Panel Efficiency:
Choose solar panels with high efficiency to maximize the power generated from the available sunlight. Higher efficiency panels are generally more expensive but can be worth the investment, especially in off-grid scenarios where space and sunlight may be limited.
Space Constraints:
Consider the available space for installing solar panels. Off-grid applications often have limited space, so choosing compact and high-output panels becomes crucial. Flexible and lightweight panels may also be suitable for installations where weight is a concern, such as on boats or RVs.
Durability and Weather Resistance:
Select solar panels that are durable and can withstand the environmental conditions of the off-grid location. Panels should be resistant to factors like rain, snow, hail, and UV radiation. Additionally, corrosion-resistant mounting hardware is important, especially in coastal or marine environments.
Battery Storage:
Integrate an efficient battery storage system to store excess energy generated during sunny periods for use during cloudy days or at night. Properly sized and high-quality batteries are essential for off-grid systems to ensure reliable power supply.
Charge Controller:
Install a charge controller to regulate the charging of batteries and prevent overcharging or deep discharging. The charge controller helps extend the lifespan of the batteries and ensures optimal performance of the overall system.
Inverter:
Use an inverter to convert DC (direct current) power generated by the solar panels and stored in batteries into AC (alternating current) power for powering household appliances. Consider the inverter’s efficiency and its compatibility with the load requirements.
System Monitoring:
Implement a monitoring system to keep track of the solar power system’s performance. This allows for early detection of issues and ensures efficient maintenance.
Budget Constraints:
Consider the budget for the off-grid solar system. While it’s important to aim for high-quality components, finding a balance between performance and cost is crucial, especially for cost-sensitive projects.
Local Regulations and Permits:
Be aware of and comply with local regulations and permit requirements for off-grid solar installations. This may include zoning restrictions, safety codes, and environmental regulations.
Solar Panel Orientation and Tilt:
Optimize the orientation and tilt angle of solar panels to capture the maximum amount of sunlight throughout the day. This may involve adjusting the tilt of the panels seasonally to account for changes in the sun’s position.
Shading Analysis:
Perform a shading analysis to identify potential shading issues from nearby trees, buildings, or other obstructions. Minimizing shading is crucial for maintaining consistent solar energy production.
Temperature Coefficients:
Consider the temperature coefficients of solar panels, which indicate how their efficiency and performance may change with temperature variations. Panels with lower temperature coefficients are generally more resilient in hotter climates.
Transportability:
For mobile off-grid applications like RVs or boats, consider the ease of transporting solar panels. Portable and foldable solar panels can be more convenient for setups that need to be moved or adjusted frequently.
By carefully considering these factors, you can effectively grade and design an off-grid solar power system that meets the specific needs and conditions of the application. Consulting with a solar professional or engineer may also be beneficial to ensure a successful off-grid solar project.
