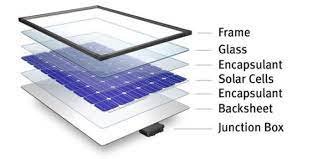
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They are a key component of solar power systems, which harness the energy from the sun to generate electricity for various applications. Here’s a comprehensive overview of solar panels:
- Basic Principle:
- Solar panels operate on the principle of the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight strikes the surface of the solar cells within the panel, it excites electrons, creating an electric current.
- Composition:
- Solar panels are typically made of silicon, a semiconductor material. There are two main types of solar panels based on the type of silicon used:
- Monocrystalline: Made from single-crystal silicon, these panels are highly efficient but more expensive.
- Polycrystalline: Composed of multiple crystals, these panels are less efficient but more cost-effective.
- Thin-Film: Made from various materials, including amorphous silicon, cadmium telluride, or copper indium gallium selenide. Thin-film panels are flexible and less expensive but generally less efficient.
- Solar panels are typically made of silicon, a semiconductor material. There are two main types of solar panels based on the type of silicon used:
- Structure:
- Solar panels consist of individual solar cells connected in a specific arrangement to form a module. Modules are then grouped together to create solar arrays.
- Efficiency:
- The efficiency of a solar panel refers to its ability to convert sunlight into electricity. Higher efficiency means that a panel can generate more electricity from the same amount of sunlight. Efficiency can vary, with commercial panels typically ranging from 15% to 22%.
- Inverter:
- Solar panels produce direct current (DC) electricity, but most household appliances use alternating current (AC). Inverters are used to convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity for use in homes and businesses.
- Installation:
- Solar panels are installed on rooftops, in solar farms, or as part of solar power plants. The panels need to be angled and positioned to maximize exposure to sunlight for optimal energy production.
- Maintenance:
- Solar panels require minimal maintenance. Periodic cleaning to remove dust and dirt is recommended to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, regular checks on the system’s overall functionality are advisable.
- Environmental Impact:
- Solar energy is considered a clean and renewable energy source, as it produces electricity without emitting greenhouse gases. However, the production and disposal of solar panels have some environmental impact, mainly due to the extraction and processing of raw materials.
- Applications:
- Solar panels are used to generate electricity for a wide range of applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial power systems. They are also employed in solar-powered water heaters, calculators, and other small electronic devices.
- Advancements:
- Ongoing research and development in the field of solar technology aim to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and explore new materials and designs for solar panels.
- Government Incentives:
- Many governments offer incentives, subsidies, and tax credits to encourage the adoption of solar energy, making it more financially attractive for individuals and businesses to invest in solar power systems.
As solar technology continues to advance, the efficiency and affordability of solar panels are likely to improve, contributing further to the growth of renewable energy sources.
